
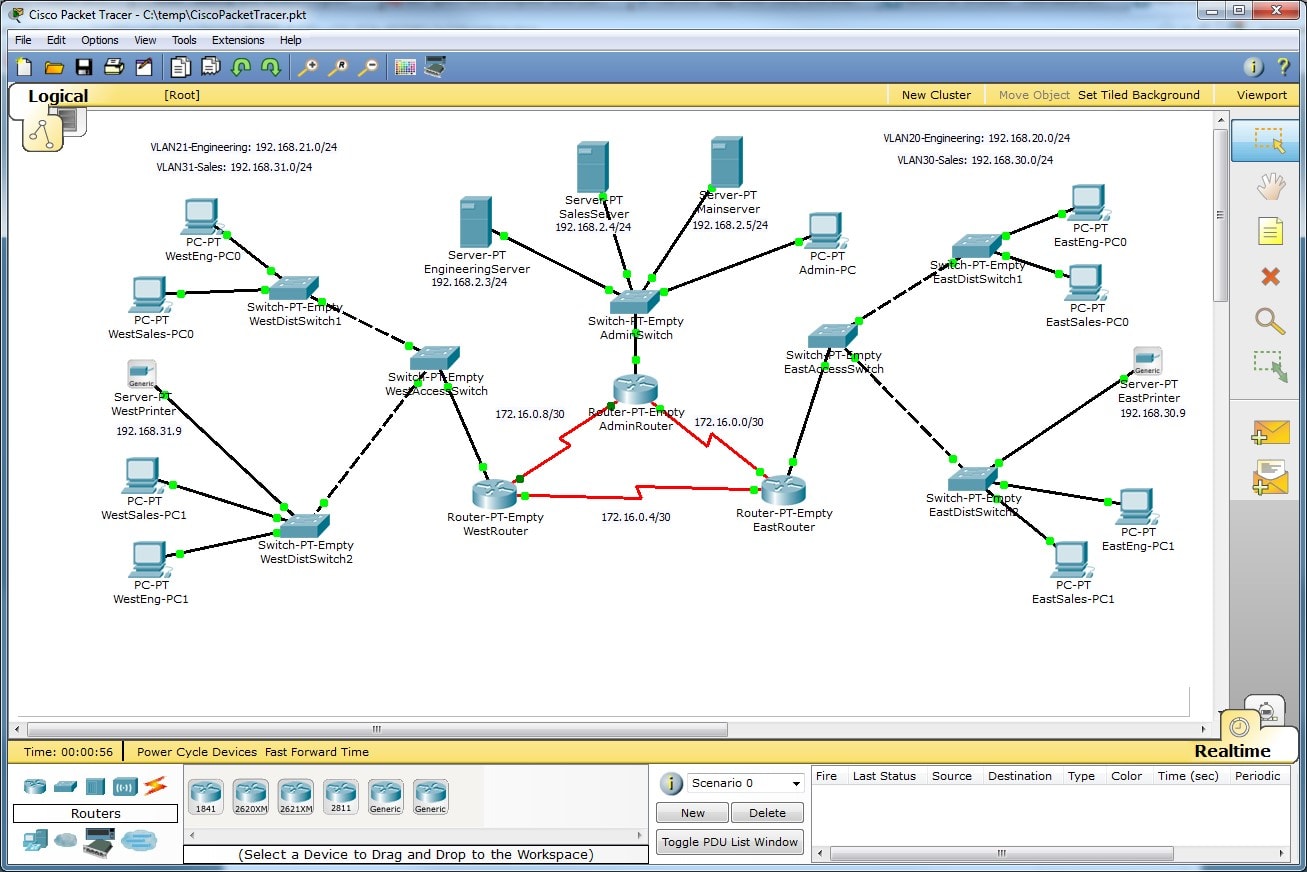
- #CCNA NETWORK VISUALIZER CLEAR ROUTER 2811 CONFIGURE HOW TO#
- #CCNA NETWORK VISUALIZER CLEAR ROUTER 2811 CONFIGURE PASSWORD#
Also, traffic exiting GigEth 0/0 will also be NAT translated. The commands above tell the router that traffic entering GigEth 0/1 will be NAT translated. This step is optional and is required only if your router acts as Internet border gateway to provide access to the internal private LAN towards the Internet.Īssume that interface GigabitEthernet 0/0 is the WAN interface (connected to ISP for Internet access) and interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 is the LAN interface connected to the internal network. My-Router# show running-config Step 6 (optional): Configure NAT You can display your current configuration to verify your settings as following: My-Router# copy running-config startup-config This will overwrite the startup configuration. Save your current running configuration into NVRAM. The default static route above instructs the router to send ALL packets that the router does not have a more specific route entry to gateway address 100.100.100.2 (which might be the ISP gateway address). The command above tells the router that network 200.200.200.0/24 is reachable via gateway address 100.100.100.2.Īnother popular static route that we usually configure on Internet Border routers is the default static route:
#CCNA NETWORK VISUALIZER CLEAR ROUTER 2811 CONFIGURE HOW TO#
Let’s see how to configure static routes from Global Configuration Mode. The administrator can assign static routes, or the router can learn routes by using a dynamic routing protocol.įor simple network topologies, static routing is preferred over dynamic routing. There are two main ways a router knows where to send packets. The Router’s main purpose is to find the best route path towards a destination network and forward packets according to the best path. Step4: Configure Routing (Static or Dynamic) My-Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/1 My-Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/0 From Global Configuration Mode you need to enter into Interface Configuration Mode: The most basic parameter for a Router Interface is the IP address. This is an essential step in order for your router to be able to forward packets in the network. Step3: Configure IP addresses for Router Interfaces
Notice that your Router prompt changes to the new hostname that you have just set. To differentiate your Router from other devices in the network, you should configure a Hostname for your device. Here I’m explaining how to configure this specific setup. Some people prefer to create also local user accounts (usernames and passwords) on the router itself in order to authenticate to the device.
#CCNA NETWORK VISUALIZER CLEAR ROUTER 2811 CONFIGURE PASSWORD#
Router(config-line)# password “strongTelnetPass” It is suggested also to configure a password for the Telnet Lines (VTY lines) which will secure your access when connecting via Telnet over the network. Router(config)# enable secret “somestrongpassword”įrom now on, when you log in from user EXEC mode you will be asked for a password.
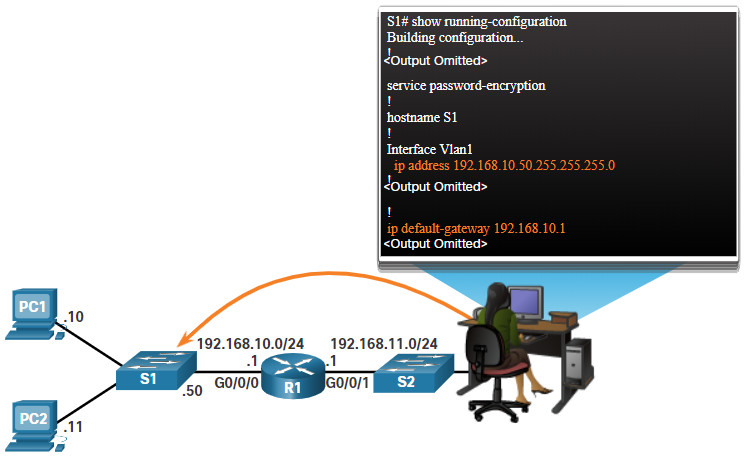
Here we will configure the Enable Secret password that you will be using from now own to enter into Privileged EXEC Mode from User EXEC Mode. In Global Configuration Mode you configure parameters that affect the whole router device. Router# configure terminal <– Privileged EXEC mode The first step is to secure your access to the router by configuring a global secret password and also passwords for Telnet or Console as needed.Įnter into Global Configuration mode from the Privileged EXEC mode: I assume that you already have some basic knowledge of CLI and how to navigate between different configuration modes (user mode, privileged exec mode etc), so let’s get started: Step-by-Step Configuration of Cisco Routers Step1: Configure Access Passwords Router(config-line)# <– Line Configuration Mode Router(config-if)# <– Interface Configuration Mode

Router(config)# <– Global Configuration Mode The basic CLI modes that we will be referring below are as following: Mastering the Cisco Router CLI is essential for more complex configuration tasks and it is the most important knowledge you should acquire if you want to become a Cisco network administrator. However, in this post I will show you how to do this basic setup with the Command Line Interface ( CLI). When you first power up a new Cisco Router, you have the option of using the “setup” utility which allows you to create a basic initial configuration. It is a step-by-step guide for the most basic configuration commands needed to make the router operational. This post is by no means an exhaustive tutorial about Cisco Routers and how to configure their numerous features.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
